Decentralized incentives
Decentralized Incentives¶
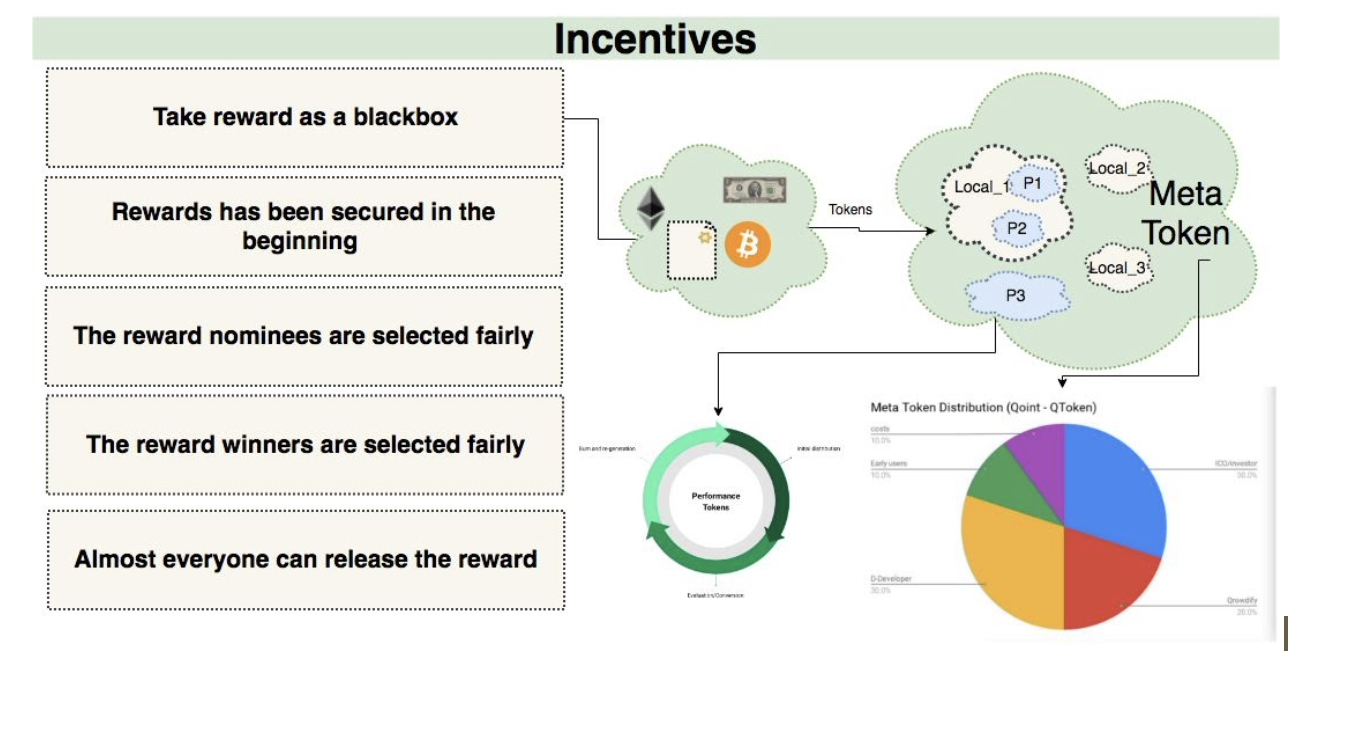
Performance Tokens¶
Performance token is used as reward for Dtask of an organization. It follows the ERC20 standard and has a limited amount for each organization. Performance token could only be gained through the Decentralized task based on the participants’ performance. Performance token could be used to pay for tickets of activities held by the organization. Thus, the performance token’s value is based on the organization’s quality. Tokens can be used for different purposes. They can be used as currency, equity or simply as a performance criteria without monetary or ownership value. Tokens also can be local or Meta tokens. Local tokens are tokens generated for a single team or community in the platform, these tokens can be exchanged to each other. Local wallets should handle the tokens generated in local communities. The Meta tokens are the main tokens that are exchangeable to local tokens. Finally the following diagram put everything together.
Badges¶
Badges are unique, ownable and verifiable tokens ( fungible) and sometime sellable.
Certificates¶
Certificates are pieces of media pdf, doc or image as certificates of achievements, knowledge or contributions. Decentralized certs' validity, ownership should be verifiable using blockchain. A certificate is one kind of reward assigned to the winners of a Dtask. It is issued by the Dtask publisher and could be endorsed by other organization members and partners. A certificate has the following data field: name, creator,content, IPFS ID, referred Dtask, endorsers and signatures. It could be used both on chain or off chain.
For the on-chain part, the creator of the Dtask has the right to create a certificate struct in Ethereum and set the content of this certificate. Other endorsers could simply call the addEndorser function to push their Ethereum account address into the list of endorsers. Since the ‘msg.sender’ represents the account where the transaction comes from, nobody could add others’ addresses into the endorser list. Therefore, the third party could view the certificate in the blockchain. The certificate could also be verified off chain. In this case, the certificate is a file with digital signatures. The creator first creates the certificate file and uploads it to IPFS. Then the creator puts the hash of the file, the IPFS ID and its signatures in the blockchain. Other endorsers could first download the IPFS file, sign it and also put their signatures in the blockchain. For off chain use, the certificate owner could send the certificate file along with signatures to the third party and the third party could verify the signatures. There still remains a problem in certificates which is the identity of endorsers and signers. The endorsement and signature of a certificate’s value comes from the endorser and signer’s identity. The endorsers’ address needs to be first registered in the smart contract and acknowledged by the leader of the organization which the Dtask belongs to. Singers also need to register their public keys in advance. In this way, the smart contract serves as a CA which helps identify the endorsers and signers.
Leadership board¶
Leaderships are updated in decentralized fashion based on a criteria. These boards are generated according to the events in the system. Awards or performance tokens. Leadership boards usually come with a deadline and incentive list describing the amount of prize the top ranked members will receive eventually.
Paths¶
Paths are like challenge board but there are couple of lists, one list per path results in different rewards for different purposes.
Challenge boards¶
Challenge boards are usually list of deliverable tasks. Challenge boards usually come with a deadline and incentive list describing the amount of prize in different situation in the challenge board.
Incentive auction¶
Incentives like badges or incentives by challenges should be able to be sold using reward marketplace.
Recommendations¶
They are statements published by individuals or organizations about other individuals and organizations. The publisher’s identity and validity of the statement should be verifiable by blockchain. The recommendation is similar to that in Linkedin. People who are familiar with someone could add comments, reviews or recommendations for him/her. In our Dtask, the creator and moderators could give recommendations to participants based on their performance in the task.